Sleep apnea, a condition that disrupts normal sleep patterns, carries significant implications for military personnel. But can it affect military enlistment? Can you join the military with sleep apnea? Can it be managed within the military?
And what about its impact on military readiness? These are questions we’ll unravel in this comprehensive exploration of sleep apnea in a military context.
Key Takeaways
-
The prevalence of sleep apnea has significantly increased among military personnel between 2005 and 2019, with deployments and disrupted sleep patterns contributing to this rise, and untreated OSA can lead to serious health complications.
-
The military has stringent medical fitness standards, often considering sleep apnea as disqualifying; however, waivers and exceptions exist if the condition is well-managed and does not impair duties.
-
Sleep apnea has considerable implications on military readiness, affecting physical performance, mental health, and injury prevention, with continuous positive airway pressure therapy being a central treatment modality.
Sleep Apnea and Military Enlistment
A silent but pervasive issue, sleep apnea has seen a 30-fold increase in prevalence among military personnel from 2005 to 2019, indicating a growing concern within the military community. The rise in sleep disorders, including sleep apnea, among military personnel is attributed to extended and more frequent deployments, especially to combat zones such as Iraq and Afghanistan. These deployments can disrupt sleep patterns, contributing to the development of sleep disorders.
Sleep apnea, particularly Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA), military medical standards, and potential waivers and exceptions for enlistment are some of the key areas that need to be addressed when discussing sleep apnea in the military context. We will further explore these key areas.
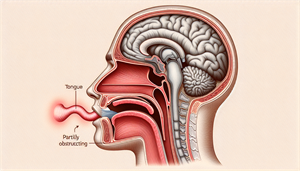
Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA)
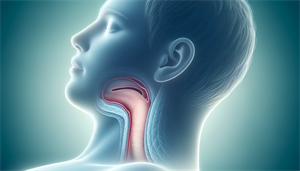
Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) is the most prevalent form of sleep apnea, characterized by:
-
Recurrent occurrences of partial or total obstruction of the upper airway during sleep
-
Sleep apnea disrupts normal sleep patterns, leading to excessive daytime sleepiness and loud snoring
-
Other indicators may include waking up with a dry mouth or sore throat, morning headaches, and difficulty breathing during sleep.
Neglecting to treat OSA, a common sleep disorder, could lead to severe health consequences, such as:
-
High blood pressure
-
Heart problems
-
Type 2 diabetes
-
Cognitive impairment
-
Reduced reaction time
-
Impaired decision-making abilities
Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP) therapy is the gold standard treatment for managing OSA symptoms, shown to lower blood pressure, reduce sleepiness, and improve overall adherence in adults with OSA.
Military Medical Standards
The Standards of Medical Fitness require individuals entering military service to adhere to specific health criteria, which apply to all branches of the military. These standards aim to ensure the absence of conditions that could disrupt military duties, including sleep apnea.
While individuals with sleep apnea may require a waiver for deployment, sleep apnea is usually deemed a disqualifying, non-waiverable medical condition for military enlistment. However, exceptions do exist, as we will explore next.
Waivers and Exceptions
In certain cases, waivers and exceptions may be granted for individuals with sleep apnea, provided the condition is well-managed and does not interfere with military duties. For instance, individuals using a CPAP device must submit a 30/60/90 day sleep analysis report as part of their medical records.
The potential impact of sleep apnea on performance is assessed through clinical evaluation, polysomnogram, and evaluation of compliance with treatment devices such as CPAP. Thus, while sleep apnea can be a barrier to military enlistment, it’s not an insurmountable one.
Managing Sleep Apnea in the Military

The control of sleep apnea in the military is fundamental for sustaining peak performance and overall health. The use of a CPAP machine, in particular, ensures a continuous flow of air during the night, preventing obstructions in the breathing passages. However, using a CPAP machine effectively requires understanding and adhering to certain steps, including:
-
Setting up the machine in a suitable location
-
Inspecting the filter
-
Connecting the hose
-
Wearing the mask for brief periods while awake to ensure comfort
-
Adjusting the settings according to your needs
-
Cleaning and maintaining the machine regularly
By following these steps, you can effectively manage your sleep apnea and improve your overall well-being.
Alternative treatments and support systems are also critical in managing sleep apnea. We will examine these components in more detail.
Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP) Therapy
CPAP therapy treats sleep apnea by maintaining positive end-expiratory pressure to prevent airway collapse and keep the airways open. This reduces apneic events, enhances oxygen saturation, and may contribute to lowering blood pressure. It’s known for its high effectiveness in managing sleep apnea symptoms, such as lowering blood pressure, reducing sleepiness, and improving overall adherence in adults.
However, getting used to a CPAP machine can take time, usually around 2 to 3 weeks. This commitment is vital for maintaining the health and performance of military personnel with sleep apnea.
CPAP Prescriptions To Veterans And Device Recall
Given the prevelance of sleep apnea in the military, the VA has distributed nearly 600,000 Philips CPAP devices to veterans. Unfortunately, these machines were linked to cancer and organ damage in 2023. As a result, the devices were recalled.
Details on the Philips CPAP Lawsuit indicate that settlement amounts could range from $100,000 to $500,000. There are alternative CPAP machines that should be considered for those impacted by the recall.
Alternative Treatments
In some cases, alternative treatments can be considered. One such treatment is Hypoglossal Nerve Stimulator Implantation (HNSI). This treatment option can be implanted and operates with minimal ancillary equipment, making it suitable for supporting active duty service members in maintaining readiness. HNSI has shown a significant success rate, with five out of eight subjects achieving surgical success, and 77% of subjects would recommend this treatment to other active duty service members.
However, bear in mind that HNSI may lead to long-term complications, such as pruritic scars and discomfort from the electric stimulation associated with this treatment.
Support Systems
Support systems within the military play an integral role in helping individuals manage their sleep apnea. These include resources and support from the VA Hospital and programs such as REVAMP, which focus on treating sleep disorders and promoting the well-being of military personnel.
Peer support systems, such as the VA TeleSleep Program, provide telemedicine services to assist veterans, particularly those in remote locations. Resources like the Veteran Training website offer valuable information on sleep apnea, including testing, treatment options, and guidance on operating necessary equipment.
Sleep Apnea Impact on Military Readiness

The effects of sleep apnea are not limited to individual health. It can considerably undermine military readiness, impacting physical performance, mental health, and injury prevention. Untreated sleep apnea can result in chronic fatigue, diminished physical endurance, and impaired cognitive abilities, all of which can impede military performance.
With the prevalence of obstructive sleep apnea among active duty service members rising from 11 per 10,000 in 2005 to 333 per 10,000 in 2019, the implications are extensive. We will examine these aspects in more detail.
Physical Performance
Untreated sleep apnea can impair physical performance in the following ways:
-
Reducing the ability to exercise
-
Lowering aerobic and anaerobic capacity
-
Exacerbating symptoms of anxiety and depression
-
Decreasing endurance in physical activities
-
Contributing to obesity, cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and neurological problems
While it may not have a substantial effect on the stamina and endurance of younger military personnel, it can adversely affect these qualities in individuals with more rigorous physical demands, such as athletes, as a result of its impact on oxygen levels.
Thus, dealing with sleep apnea is not only about managing a medical condition but also about maintaining physical performance and reducing the risk of injuries.
Mental Health
Sleep apnea can also exert a notable influence on the mental health of soldiers, particularly in terms of depression and anxiety. Adequate sleep plays a significant role in promoting both physical and mental well-being, underscoring the importance of addressing sleep apnea for mental health within the military.
The mental health issues resulting from sleep apnea have a significant impact on military readiness as they affect:
-
Operational readiness
-
Personnel health
-
Wellbeing
-
Contribute to the severity of conditions such as PTSD, anxiety, depression, and chronic pain.
Injury Prevention
Sleep apnea-induced fatigue contributes to an elevated risk of injuries as it can result in impairments in attention, alertness, and motor coordination. These impairments can manifest in a greater propensity for motor vehicle and workplace accidents, as well as musculoskeletal injuries that are particularly common among military personnel.
Effectively managing sleep apnea through interventions like positive airway pressure therapy has several benefits, including:
-
Decreasing the frequency of breathing interruptions during sleep
-
Reducing daytime sleepiness
-
Decreasing the likelihood of accidents and injuries caused by sleep deprivation.
Sleep Apnea in Veterans
Sleep apnea is a common issue among veterans, with apnea, insomnia, and nightmares being the most frequently identified types of sleep disorders. As veterans transition to civilian life, the management of sleep apnea is often an ongoing challenge. This is particularly true when it comes to managing symptoms such as:
-
loud snoring
-
gasping for air during sleep
-
waking up with a dry mouth
-
morning headaches
-
excessive daytime sleepiness
We’ll examine this transition and the resources veterans have at their disposal for managing sleep apnea.
Transition to Civilian Life
Veterans with sleep apnea may face challenges in adjusting to civilian life, including managing their condition without the structured support of the military. While the VA offers support to veterans to enhance their sleep quality, including the management of their sleep apnea, veterans also need to make lifestyle changes, such as:
-
weight reduction
-
cessation of alcohol and smoking
-
adherence to a nutritional diet
-
regular exercise
These changes can positively impact the management of sleep apnea.
The stress associated with transitioning to civilian life can worsen sleep apnea symptoms. However, veterans who have PTSD in addition to a new diagnosis of sleep apnea frequently experience a notable decrease in PTSD symptoms, sleepiness, and depression.
VA Benefits and Resources
The Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) offers benefits and resources to help veterans with sleep apnea. This includes:
-
Health care
-
Disability compensation based on the severity of their condition, with disability ratings ranging from 0% to 100%
-
Veterans with severe symptoms may receive a 100% disability rating.
Furthermore, the VA may also provide coverage for the cost of hypoglossal nerve stimulator implantation surgery for veterans with sleep apnea.
Prevention and Awareness
Preventing and being aware of sleep apnea are key for preserving the health and readiness of military personnel. Quality sleep holds significance for military personnel due to the potential adverse effects of sleep deprivation and conditions such as:
-
obstructive sleep apnea
-
insomnia
-
restless leg syndrome
-
narcolepsy
on concentration, decision-making capabilities, and overall health.
Thus, maintaining proper sleep hygiene and addressing poor sleep through consistent checkups are of utmost importance.
Sleep Hygiene
Sleep hygiene encompasses both the sleep environment and behavior. Maintaining good sleep hygiene can lower the likelihood of developing sleep apnea and enhance the overall quality of sleep. Recommended practices for maintaining good sleep hygiene include:
-
Establishing a consistent sleep schedule
-
Adhering to a nightly routine
-
Fostering healthy daily habits
-
Optimizing the sleep environment
-
Minimizing electronic exposure
-
Abstaining from stimulants
-
Ensuring a comfortable sleep environment
-
Managing stress and anxiety
-
Engaging in regular exercise
-
Limiting daytime naps
Regular Checkups
Regular checkups play a crucial role in the management and treatment of sleep apnea in the military, as they have the potential to enhance both physical and mental well-being. Routine examinations, such as home sleep testing and nocturnal polysomnography, are suggested for diagnosing sleep apnea.
The suggested frequency of medical checkups for sleep apnea in military personnel may vary, but the significance of these checkups is undeniable.
Summary
Sleep apnea is a pervasive issue in the military, affecting both active-duty personnel and veterans. Its impacts range from individual health to military readiness, underscoring the importance of prevention, management, and awareness.
From understanding Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA), Military Medical Standards, and potential waivers and exceptions, to exploring the management of sleep apnea in the military through Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP) Therapy, alternative treatments, and support systems, we have delved into various facets of this crucial topic.
The road to combating sleep apnea in the military may be challenging, but it’s not insurmountable. With the right knowledge, resources, and support, both military personnel and veterans can effectively manage this condition and maintain their readiness and well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is sleep apnea disqualifying?
Yes, sleep apnea can be disqualifying for certain occupations, as it can affect safe driving and cognitive function. Successful treatment can reinstate one's qualified status.
What can disqualify you from joining the military?
Illegal drug use, alcohol dependence, height/weight requirements, certain contagious diseases, and law violations, such as a conviction that prohibits carrying a firearm, can disqualify you from joining the military. Additionally, your medical history, physical fitness level, educational background, or history of mental illness may also be disqualifying factors.
How do you prove sleep apnea is military related?
To prove sleep apnea is military related, you need to have a diagnosis through a sleep study and show that the condition started during military service or has a connection to an event or exposure during military service. It can also be considered a secondary service-connected condition.
Does sleep apnea qualify as a disability?
No, the SSA does not recognize sleep apnea as a disability, but you may still qualify for benefits if your sleep disorder causes other severe symptoms that meet the SSD's definition of disabled. Therefore, you may qualify for benefits if your sleep disorder causes severe enough symptoms.
What disqualifies you from the draft?
Having certain diseases or infirmities can disqualify you from the draft.