Waking up with a dry mouth and a longing for better sleep? This article dives right into “how to breathe through nose while sleeping”, with a focus on overcoming common barriers to nasal breathing.
We’ll cover effective strategies, from managing nasal congestion to adjusting your sleep position, to ensure that you can transition to healthier sleep habits and wake up feeling rested.
Key Takeaways
-
Nasal breathing during sleep is vital for optimal oxygen intake and overall health, while mouth breathing can lead to adverse health effects including sleep disorders and daytime fatigue.
-
Physical obstructions like a deviated septum, enlarged turbinates, and nasal congestion, as well as mental factors like stress, can cause mouth breathing, highlighting the need to address these issues for better sleep.
-
Strategies to encourage nasal breathing include addressing nasal congestion, adjusting sleep position, incorporating breathing exercises, using nasal strips and dilators, and seeking medical help if symptoms persist.
The Importance of Nasal Breathing During Sleep

Nasal breathing, also known as nose breathing, is the body’s preferred method of respiration, particularly crucial during sleep. It facilitates optimal oxygen intake and serves to filter and warm the breath, leading to an overall improvement in the body’s oxygenation.
On the flip side, mouth breathing, characterized by breathing through the mouth instead of the nose, can have adverse effects on sleep quality, such as causing a dry mouth, a scratchy throat, and a sense of inadequate rest. Continued mouth breathing can escalate to serious health problems, highlighting the importance of encouraging nasal breathing to counteract mouth breathing.
Advantages of Nasal Breathing
The physiological mechanisms associated with nasal breathing encompass:
-
Warming and humidifying the air as it passes through the nasal airway
-
Conditioning of the inspired air
-
Supporting immune defense
-
Optimal oxygen absorption
-
Contributing to overall health benefits.
Besides, nasal breathing offers several benefits, including:
-
Significantly reducing the likelihood of snoring, leading to a quieter sleep environment compared to mouth breathing at night
-
Improving the quality of rest and recovery during sleep by regulating sleep
-
Decreasing the chance of snoring and sleep apnea
-
Supporting a more restful good night’s sleep.
Health Risks of Mouth Breathing
Mouth breathing during sleep can result in sleep disorders such as snoring, obstructive sleep apnea, high blood pressure, along with daytime fatigue. In children, mouth breathing and snoring may indicate underlying health issues that could be serious, necessitating medical attention. This is especially true if accompanied by symptoms such as morning headaches, difficulty concentrating, or a recurrence of bed-wetting.
Furthermore, mouth breathing can cause dry mouth and bad breath by enabling bacterial growth due to reduced saliva production. It is thus important to educate both children and adults to keep their mouth shut while sleeping to stop mouth breathing.
Identifying the Causes of Nighttime Mouth Breathing
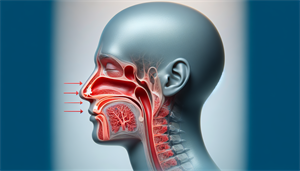
Understanding the root causes of mouth breathing is the first step towards finding a solution. Physical factors that may result in mouth breathing during sleep include nasal obstruction from conditions such as a deviated septum, enlarged turbinates, and nasal polyps.
Conversely, mental factors like stress and anxiety can trigger mouth breathing by activating the body’s fight-or-flight response, leading to mouth instead of nasal breathing during sleep. Therefore, pinpointing these issues is crucial in minimizing mouth breathing while asleep.
Physical Factors
Physical factors that contribute to mouth breathing are often related to obstruction in the nasal passages. A deviated septum, a condition where the thin wall between the nasal passages is displaced to one side, can lead to impaired nasal breathing during sleep, resulting in mouth breathing.
Moreover, conditions like enlarged turbinates and nasal congestion, commonly caused by colds or allergies, restrict airflow through the nasal passages, leading to difficulty in nasal breathing. When the nose is obstructed, the body naturally resorts to mouth breathing to ensure adequate oxygen levels, especially during sleep when breathing is less consciously regulated.
Mental Factors
Mental factors also play a significant role in inducing mouth breathing. Psychological factors such as stress and anxiety can induce mouth breathing by stimulating the flight-or-fight response. This response activates the sympathetic nervous system, which encourages mouth breathing as a less regulated form of respiration.
Stress and anxiety can lead to mouth breathing as they activate the sympathetic nervous system, which governs the fight-or-flight response. This can cause rapid and shallow breathing, resulting in mouth breathing. Therefore, addressing these mental factors can help promote nasal breathing during sleep.
Strategies to Encourage Nasal Breathing While Sleeping

Effective strategies that address nasal congestion, adjust sleep position, and incorporate breathing exercises are crucial in transitioning from mouth to nasal breathing during sleep.
By addressing the root causes of mouth breathing, these strategies can help improve sleep quality, minimize sleep disruptions, and contribute to better overall health. After all, a good night’s sleep is not just about the number of hours you sleep, but also about the quality of that sleep, which can be significantly impacted by the way you breathe.
Addressing Nasal Congestion
One of the effective ways to promote nasal breathing during sleep is to address nasal congestion, which may obstruct the nasal passageways and lead to mouth breathing. This can be achieved by using saline sprays, avoiding eating close to bedtime, and treating allergies.
Nasal saline irrigation, for instance, can effectively draw out excess fluid from the nasal membrane and serve as a gentle decongestant, thereby assisting in the alleviation of nighttime nasal congestion. Additionally, avoiding eating close to bedtime can help to prevent the development of congestion that could obstruct nasal breathing during sleep.
Adjusting Sleep Position
Another effective strategy to reduce mouth breathing and promote nasal breathing during sleep, ensuring a good night’s sleep, is adjusting the sleep position. Sleeping on the side or with the head elevated can aid in improving airway function and minimizing mouth breathing.
Elevating the head has the potential to widen the airways, thereby enhancing nasal breathing and potentially mitigating mouth breathing. Utilizing a higher pillow can effectively elevate the head, thus opening up the airways and facilitating nasal breathing during sleep.
Incorporating Breathing Exercises
Breath work and breathing exercises are essential in conditioning the body to transition from mouth breathing to nasal breathing and are therefore integral in promoting nasal breathing during sleep.
Exercises such as the 4-7-8 breathing technique, alternate nostril breathing, and nasal breathing exercises can help train the body to breathe through your nose during sleep. In addition, taking deep breaths through the nose throughout the day can alleviate nasal congestion and facilitate easier nasal breathing.
Products and Devices to Support Nasal Breathing
In addition to the strategies mentioned above, there are several products and devices available that can further support nasal breathing during sleep. These include nasal strips and dilators, as well as sleep positioning aids.
These products work by widening the nostrils or raising the head, improving the flow of air into the nasal passages. They can be particularly helpful for individuals with chronic nasal congestion or those who struggle to maintain a sleep position that promotes nasal breathing.
Nasal Strips and Dilators
Nasal strips and dilators can be particularly helpful for those struggling with nasal congestion. They work by physically expanding the nostrils, enhancing airflow through the nasal airways, and alleviating congestion by improving the blood vessels’ functionality in the nasal area.
The effectiveness of these products varies from person to person. However, some studies suggest that they may reduce nasal congestion and enhance sleep quality, while others have not found significant improvements in nasal congestion, sleep quality, or sleep-disrupted breathing.
Sleep Positioning Aids
Sleep positioning aids are specifically designed to assist individuals in maintaining a sleep position that minimizes mouth breathing and fosters nasal breathing. These aids include a variety of products, such as specially engineered pillows and wearable devices.
These positioning aids work in combination with items such as nasal strips and dilators to enhance sleep quality by facilitating proper breathing. They are a practical solution for those who find it challenging to maintain a sleep position that encourages nasal breathing.
When to Seek Medical Help
While the mentioned strategies and aids can provide significant relief, remember not to overlook persistent symptoms like mouth breathing and snoring. If such symptoms persist, seeking medical guidance for a sleep apnea diagnosis and appropriate treatment becomes necessary.
Moreover, if you’re uncertain about the underlying cause of your mouth breathing, it’s advisable to consult a healthcare provider. Medical professionals specialized in diagnosing sleep apnea include:
-
cardiologists
-
neurologists
-
somnologists
-
sleep medicine doctors
Diagnosing Sleep Apnea
Characterized by repetitive breathing interruptions during sleep, sleep apnea is a potentially critical sleep disorder. Symptoms such as:
-
severe fatigue
-
daytime drowsiness
-
irritability
-
excessive daytime sleepiness
-
distinctly loud snoring
could indicate sleep apnea.
Diagnosis is typically conducted through a test known as polysomnography, which monitors different bodily functions during sleep. In certain instances, this test can be conducted at home with simplified tests. Therefore, it’s important to consult with a healthcare provider if you’re experiencing persistent symptoms of sleep apnea.
Surgical Options
In some cases, surgical interventions may be necessary to address chronic mouth breathing. Typical surgical interventions include:
-
Surgical jaw expansion
-
Orthodontic treatments
-
Adenoidectomy
-
Septoplasty
-
Turbinate reduction
-
Mouth taping (in some non-surgical cases)
-
Others
The removal of nasal polyps or swollen adenoids can significantly improve chronic mouth breathing by enhancing dentofacial development and lowering the likelihood of respiratory tract infections. However, it’s important to consider the potential risks and benefits associated with the decision to undergo surgery for chronic mouth breathing.
Tips for Maintaining Good Oral Health
Good oral health, which is integral in preventing and managing mouth breathing, can be maintained through regular dental checkups, ideally twice a year, to monitor potential issues that may lead to mouth breathing.
In addition to regular dental checkups, maintaining proper oral hygiene is key. This includes brushing teeth twice a day for approximately 2 minutes using a fluoride toothpaste and daily flossing. These practices can help to prevent dental issues that may contribute to or exacerbate mouth breathing.
Summary
In conclusion, nasal breathing is the body’s natural and preferred method of respiration, particularly during sleep. Mouth breathing can have adverse effects on sleep quality and health, leading to sleep disorders, high blood pressure, and daytime fatigue. Therefore, it’s essential to implement strategies and use aids to encourage nasal breathing during sleep. Regular dental checkups and maintaining proper oral hygiene are also crucial in preventing and managing mouth breathing. Remember, a good night’s sleep isn’t just about the quantity, but also the quality of sleep, which can be significantly impacted by the way you breathe.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do I stop mouth breathing at night?
To stop mouth breathing at night, try treating the underlying cause such as nasal congestion with remedies like humidifiers or nasal saline sprays. This can help reduce the need for mouth breathing and improve your sleep quality.
What is the importance of nasal breathing during sleep?
Nasal breathing during sleep is important as it facilitates optimal oxygen intake, filters and warms the breath, leading to improved oxygenation, and reduces the likelihood of snoring for a quieter sleep environment.
When should I seek medical help for mouth breathing during sleep?
If you continue to experience mouth breathing and snoring during sleep, it is important to seek advice from a medical professional for a sleep apnea diagnosis and appropriate treatment. If you're unsure about the cause of the mouth breathing, it's best to consult a healthcare provider.
What are some surgical options for addressing chronic mouth breathing?
Surgical options for chronic mouth breathing include surgical jaw expansion, orthodontic treatments, adenoidectomy, septoplasty, and turbinate reduction. Consider the potential risks and benefits before undergoing surgery.


