Sleep apnea – a common sleep disorder that can significantly impact your life and wellbeing. But what if there was a way to better understand this condition, its types, causes, and effects on health, and ultimately find the most suitable treatment plan?
In this blog post, we’ll explore sleep apnea from the inside out, allowing you to make informed decisions and improve your quality of life.
Join us on a journey to uncover the secrets of sleep apnea, from the two main types - obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) and central sleep apnea (CSA) - to the challenges in diagnosing and treating this sleep disorder.
Get ready to embark on a path toward a better understanding of sleep apnea and a healthier, more restful future.
Key Takeaways
-
Understand the two main types of sleep apnea (OSA and CSA) to determine suitable treatments.
-
Recognize signs & symptoms, risk factors, and effects on health for OSA & CSA to improve overall wellbeing.
-
Seek professional help from a Sleep Specialist for diagnosis and treatment plans tailored to individual needs.
Sleep Apnea Probability Calculator
Answer the following questions to assess your risk of Obstructive Sleep Apnea:
Understanding the Two Main Types of Sleep Apnea
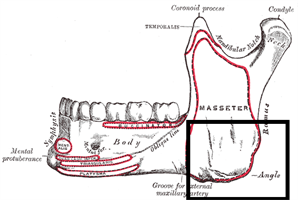
Sleep apnea is a sleep disorder characterized by recurrent pauses in breathing during sleep, affecting countless people with sleep apnea worldwide, including those with severe sleep apnea.
People often wonder, “how is sleep apnea categorized?” Sleep apnea predominantly falls into two categories: obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) and central sleep apnea (CSA). Despite sharing common symptoms, understanding their distinct differences is key to determining suitable treatment options.
OSA occurs when the throat muscles relax and block the airway during sleep, leading to snoring, gasping, and frequent awakenings. On the other hand, CSA is a rarer condition where the brain fails to send proper signals to control breathing, resulting in shallow breaths and sleep disruptions. We’ll further examine each sleep apnea type to understand their unique characteristics and health effects better.
Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA)
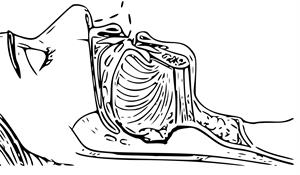
Obstructive sleep apnea occurs when the relaxation of muscles in the back of the throat during sleep results in a decreased airway for air to pass through. This blockage leads to loud snoring, gasping, and frequent awakenings, often going undiagnosed. OSA can range from mild sleep apnea to severe, with potential risk factors including obesity, smoking, alcohol consumption, and age.
OSA profoundly impacts health and daily life, leading to fatigue, difficulty concentrating, and a heightened risk of cardiovascular diseases, including stroke and heart attack. More severe cases can lead to even more serious health issues, underscoring the need for prompt and effective response to this condition.
Central Sleep Apnea (CSA)
Central Sleep Apnea, unlike OSA, is not caused by a blocked airway but rather by a failure of the brain to transmit proper signals to regulate breathing. As a result, individuals with CSA experience shallow breaths and sleep disruptions. The indications of CSA may not be readily apparent unless highlighted by a bed partner or caregiver, making it challenging to diagnose without proper evaluation.
Central Sleep Apnea can be addressed through various treatment options, depending on the underlying cause. Some therapies include transvenous phrenic nerve stimulation, a method for treating sleep apnea in cases where CPAP therapy is not effective.
Pinpointing and tackling the root cause of CSA is pivotal to providing the person in question with the most suitable and beneficial treatment.
Identifying Sleep Apnea Symptoms
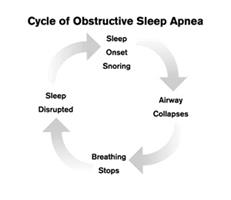
Recognizing the symptoms of sleep apnea, especially in cases of undiagnosed sleep apnea, can be tricky due to the overlapping signs between OSA and CSA, including snoring, gasping, and daytime fatigue. Acknowledging these symptoms promptly is crucial for obtaining medical help and enhancing sleep quality and overall health.
Since the symptoms of OSA and CSA can be quite similar, it is essential to consult a sleep specialist to differentiate between the two conditions and receive an accurate diagnosis. We’ll examine the shared symptoms between OSA and CSA and the complications they raise in diagnosing the sleep apnea type without a proper evaluation.
Overlapping Symptoms
The similarity of symptoms between OSA and CSA can make it challenging to accurately identify the type of sleep apnea without proper evaluation. Common symptoms shared by both OSA and CSA include snoring, daytime sleepiness, and difficulty concentrating. Accurate diagnosis not only helps determine the specific type of sleep apnea but also enables the sleep specialist to recommend appropriate treatment options.
Understanding the overlapping symptoms between OSA and CSA not only helps raise awareness about the challenges in diagnosing sleep apnea but also highlights the importance of seeking professional help. A sleep specialist can provide the necessary evaluation and expertise to ensure the most effective treatment plan is implemented.
Risk Factors Associated with Sleep Apnea
Various factors can influence an individual’s risk of developing sleep apnea, and these elements differ between OSA and CSA. Identifying and addressing these risk factors can significantly improve sleep quality and reduce the chances of developing sleep apnea or related complications.
We’ll scrutinize the risk factors related to OSA and CSA to comprehend the variations between these two sleep apnea types and their potential triggers more clearly.
Obstructive Sleep Apnea Risk Factors
Risk factors for OSA include:
-
Obesity: can lead to narrowing of the airway and an increased risk of collapse
-
Age: the risk of OSA increases with age, likely due to alterations in the anatomy of the upper airway
-
Gender: men are more likely to experience OSA than women due to anatomical differences in the upper airway
-
Anatomical characteristics of the head and neck area: features such as a large tongue, a small jaw, or a large neck circumference can contribute to an increased risk of OSA.
Other factors associated with an increased risk of OSA include smoking, alcohol use, and certain medications. Being aware of these risk factors can help individuals take necessary precautions to prevent or manage OSA effectively.
Central Sleep Apnea Risk Factors
In contrast to OSA, CSA risk factors involve medical conditions affecting the brain stem, heart or kidney failure, and stroke. Conditions such as Parkinson’s disease and other neurological diseases can affect the brain stem. Age, sex, lifestyle, and certain medications are potential risk factors for heart or kidney failure.
High blood pressure, smoking, diabetes, and high cholesterol are potential risks factors for stroke.
Understanding the risk factors associated with CSA can help individuals and healthcare professionals identify potential triggers, implement preventative measures, and tailor appropriate treatment plans to address the underlying cause of the condition.
The Impact of Sleep Apnea on Health and Daily Life
Sleep apnea can have significant effects on both mental and physical health, impacting daily life and increasing the risk of various health complications. Recognizing symptoms and seeking suitable treatment is pivotal to reducing the negative impact of sleep apnea on overall wellbeing and life quality.
Factors:
-
We’ll discuss how sleep apnea influences mental and physical health
-
Highlighting the potential challenges encountered by individuals with this sleep disorder
-
The necessity of prompt intervention
Effects on Mental Health
Mental health effects of sleep apnea include mood swings, depression, and difficulty concentrating. Research suggests that sleep apnea can cause disrupted sleep, leading to depressed mood, increased stress, and heightened levels of anxiety. Sleep apnea has also been linked to psychiatric comorbidity, which is defined as the presence of two or more mental health disorders in an individual.
Addressing sleep apnea and its symptoms can markedly enhance mental health and overall wellbeing. Pursuing professional assistance and applying suitable treatment plans is crucial in managing sleep apnea’s mental health effects.
Effects on Physical Health
Physical health effects of sleep apnea include:
-
High blood pressure: Sleep apnea can cause the body to produce hormones that constrict blood vessels, leading to elevated blood pressure.
-
Heart problems: Sleep apnea may result in the production of hormones that can lead to an irregular heartbeat, as well as an increased risk of stroke and heart attack.
-
Increased risk of accidents: Sleep apnea can cause excessive daytime sleepiness, which can increase the risk of accidents while driving or operating machinery.
Additionally, sleep apnea has the potential to increase the risk of accidents due to fatigue and drowsiness, reducing a person’s capacity to safely drive or operate machinery. Addressing the physical health effects of sleep apnea is crucial in maintaining overall health and safety, making it vital to seek appropriate treatment and intervention.
Diagnosing Sleep Apnea: Sleep Studies and Medical Evaluations
Diagnosing sleep apnea involves sleep studies and medical evaluations, often conducted by sleep specialists. A thorough evaluation of symptoms, physical examination, and sleep studies can help get sleep apnea diagnosed, differentiate between OSA and CSA, determine the severity of the condition, and guide the most appropriate treatment plan.
We’ll delve into the diagnostic process for sleep apnea and appreciate the vital role that sleep specialists play in providing precise diagnoses and customized treatment options.
The Role of Sleep Specialists
Sleep specialists play a crucial role in diagnosing sleep apnea and determining the most appropriate treatment options. These medical professionals have undergone specialized training in sleep medicine and are knowledgeable about all aspects of sleep. Their primary aim is to accurately diagnose and treat sleep disorders.
Sleep specialists typically conduct a physical exam, a sleep study, and a review of medical history to diagnose sleep apnea. Additional tests may be ordered to rule out other conditions. Consulting with a sleep specialist ensures that the most suitable treatment plan is implemented, ultimately improving sleep quality and overall health.
Treatment Options for Sleep Apnea
Various treatment options are available for sleep apnea, with specific treatments depending on the type of sleep apnea and its severity. Comprehending different treatment options is crucial towards implementing the most suitable and effective plan, boosting sleep quality and overall wellbeing in the long run.
We’ll examine treatment options for both OSA and CSA, shedding light on the most effective methods to address sleep apnea and promote healthier, more restful sleep.
Treating Obstructive Sleep Apnea
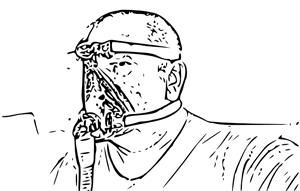
Obstructive sleep apnea treatments, which aim to treat sleep apnea, include continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) machines, oral appliances, and surgery. CPAP therapy involves wearing a mask over the nose and mouth while sleeping, connected to a machine that provides a constant flow of air into the airways to keep them open. This flow of air creates a positive air pressure, helping to prevent the collapse of the airways. Oral appliances, on the other hand, are devices designed to be worn in the mouth during sleep to maintain open airways in mild to moderate cases of sleep apnea.
In some cases, surgery may be an option to remove any tissue impeding the airways. Additionally, lifestyle changes such as weight loss and altering sleep positions can help lessen the intensity of sleep apnea. A consultation with a healthcare professional is vital to establish the most appropriate treatment plan for each individual case.
Mouthpieces vs. CPAP
Mouthpieces can be an alternative to CPAP for some patients with mild to moderate OSA, but CPAP remains the most effective treatment for severe cases.
Mouthpieces are designed to help maintain the position of the jaw and tongue in order to reduce pressure on the airway. Although mouthpieces may provide effective relief for mild to moderate OSA, CPAP may be more beneficial for more severe cases.
The choice between a mouthpiece and CPAP therapy should be made in consultation with a healthcare professional, considering the severity of OSA and the individual’s specific needs. Appropriate guidance and support play a crucial role in determining the best treatment option.
Treating Central Sleep Apnea
Central sleep apnea treatments focus on addressing the underlying medical issue and may include PAP devices, supplemental oxygen therapy, or medications to improve breathing.
PAP therapy, like CPAP, involves wearing a mask over the nose and mouth while sleeping, connected to a machine that provides a continuous flow of air into the airways. Supplemental oxygen is another form of treatment that involves the use of a machine to provide a continuous flow of oxygen through a mask that is placed over the nose and/or mouth.
Weight loss can also help reduce the severity of central sleep apnea, as it reduces the amount of fat in the neck and throat area, thus aiding in keeping the airway open during sleep. It’s crucial to seek advice from a healthcare professional to establish the most suitable treatment plan for central sleep apnea, taking into account the condition’s root cause.
Summary
In this blog post, we have explored the complex world of sleep apnea, including its types, symptoms, risk factors, effects on health, diagnosis, and treatment options. By understanding the different aspects of sleep apnea, you can take the necessary steps to improve your sleep quality, overall health, and daily life.
Remember, seeking professional help and implementing appropriate treatment plans are essential in managing sleep apnea effectively. With the right guidance and support, you can overcome the challenges of sleep apnea and embark on a journey toward a healthier, more restful future.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are 3 symptoms of sleep apnea?
Sleep apnea symptoms include daytime sleepiness, loud snoring, observed episodes of stopped breathing during sleep, waking during the night and gasping or choking, morning headaches, difficulty focusing during the day, mood changes, and a dry mouth or sore throat.
What is the main cause of sleep apnea?
The primary cause of sleep apnea is related to age, sex, body weight, and certain anatomical features of the head and neck area, with obesity and excess weight being particularly common risk factors in adults.
How do you know if you have sleep apnea?
If you experience loud snoring, pauses in breathing, waking up abruptly with shortness of breath, having a dry or sore throat when you awake, difficulties with memory and concentration, unusual moodiness or irritability, and your bed partner notices you stop breathing, these may be signs of underlying obstructive sleep apnea.
Is sleep apnea very serious?
Sleep apnea is very serious, as it can lead to long-term complications such as high blood pressure, diabetes, heart disease, depression, memory problems and increased risk of accidents. Moreover, there have been some high-profile deaths linked to sleep apnea, so early diagnosis and treatment are vital in order to avoid more serious consequences. Treatments such as positive airway pressure devices are often effective when used regularly.
What are the two primary types of sleep apnea?
The two primary types of sleep apnea are obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) and central sleep apnea (CSA). OSA occurs when the airway is blocked due to tissue collapse, while CSA is caused by a lack of communication between the brain and the muscles that control breathing.
References
- Obstructive Sleep Apnea. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK459252/
- Obstructive Sleep Apnea: A Growing Problem. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3096276/
- Obstructive Sleep Apnea, The Not-So-Silent Killer. https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.119.316359